# ArkUI Overview
ArkUI is a UI development framework for building OpenHarmony applications. It provides effortlessly natural UI syntax and UI development infrastructure including UI components, animation mechanisms, and event interaction, to meet the visualized GUI development requirements of application developers.
## Basic Concepts
- **Component**: the smallest unit for UI building and display. You build a UI that meets your needs through flexible combinations of components.
- **Page**: the smallest unit for ArkUI application scheduling. You can design multiple pages for your application, manage their files on a per-page basis, and schedule page redirection through [page routing](../reference/apis/js-apis-router.md) APIs, so as to implement decoupling of application functions.
## Key Features
- **UI components**: ArkUI comes with a diverse array of built-in polymorphic components, including basic components (such as text, image, and button), container components with one or more child components, drawing components allowing for customization, and media components that provide video playback capabilities. By being polymorphic, a component provides variant forms to adapt to different types of devices and platforms.
- **Flexible layouts**: Creating a responsive UI in ArkUI is easy, with the carefully-designed layout approaches: Besides the basic linear and flexible layouts, you also have access to the advanced list, grid, and column grid layouts as well as the atomic layouts that auto-adapt to screen resolutions.
- **Animation**: Apart from animations embedded in components, ArkUI offers additional animation features: attribute animation, transition animation, and custom animation.
- **Drawing**: ArkUI offers advanced drawing capabilities that allow you to draw custom shapes with a range of editors, from images to fill colors and texts.
- **Interaction**: ArkUI allows users to interact with your application UI properly, regardless of the system platform and input device. By default, the UI accepts input from touch gestures, remote controls, keyboards, and mouse devices, with support for event callbacks where you can define interaction logic of your own.
- **Platform API channel**: ArkUI provides an API extension mechanism through which platform capabilities are encapsulated to produce JavaScript (JS) APIs in a unified style.
- **Two development paradigms**: ArkUI comes with two development paradigms: [ArkTS-based declarative development paradigm](./ui-ts-overview.md) (declarative development paradigm for short) and [JS-compatible web-like development paradigm](./ui-js-overview.md) (web-like development paradigm for short). You can choose whichever development paradigm that aligns with your practice.
| Development Paradigm | Description | Applicable To | Target Audience |
| -------- | ---------------------------------------- | ---------------- | ------------------- |
| Declarative development paradigm | Uses [ArkTS](../quick-start/arkts-get-started.md) – a superset of TypeScript with declarative UI syntax, providing UI drawing capabilities from three dimensions: component, animation, and status management. The programming mode used is closer to natural semantics. You can intuitively describe the UI without caring about how the framework implements UI drawing and rendering, leading to simplified and efficient development.| Applications involving technological sophistication and teamwork| Mobile application and system application developers|
| Web-like development paradigm| Uses the classical three-stage programming model, in which OpenHarmony Markup Language (HML) is used for building layouts, CSS for defining styles, and JS for adding processing logic. UI components are associated with data through one-way data-binding. This means that when data changes, the UI automatically refreshes with the new data. This development paradigm has a low learning curve for frontend web developers, allowing them to quickly transform existing web applications into ArkUI applications.| Small- and medium-sized applications and service widgets with simple UIs | Frontend web developers |
## Framework Structure
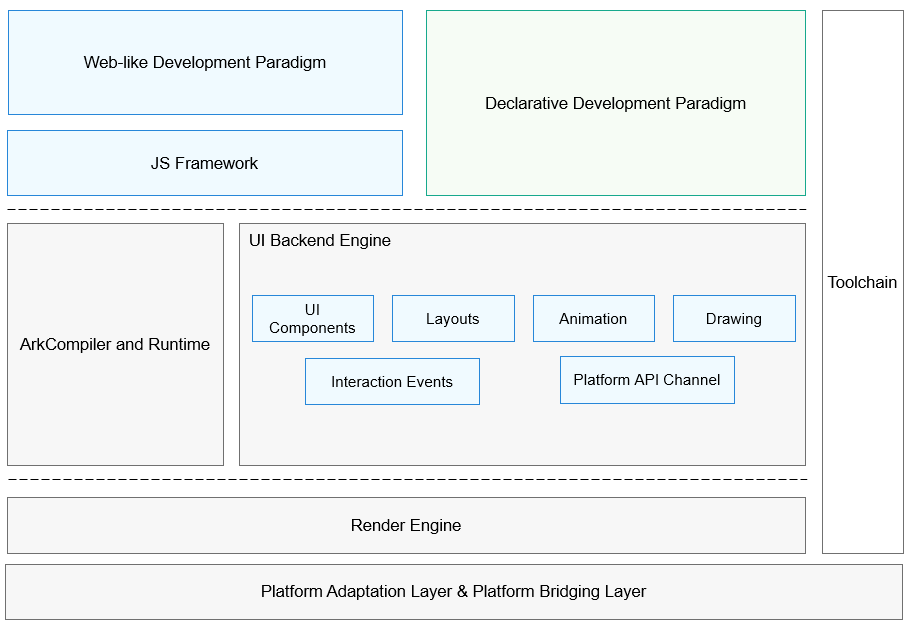
As shown above, the two development paradigms share the UI backend engine and language runtime. The UI backend engine implements the six basic capabilities of ArkUI. The declarative development paradigm does not require the JS Framework for managing the page DOM. As such, it has more streamlined rendering and update links and less memory usage. This makes the declarative development paradigm a better choice for building application UIs.
## Relationship Between UI and Ability Framework
OpenHarmony provides two application models: FA model and stage model. The table below describes the relationship between these two models and the two development paradigms of ArkUI.
**FA Model**
| Type | UI Development Paradigm | Description |
| ---- | -------- | ---------------------------------------- |
| Application | Web-like development paradigm| UI development: HML, CSS, and JS
Service entries: files with fixed file names, which are **app.ets** (Page ability), **service.ts** (Service ability), and **data.ts** (Data ability)
Service logic: JS and TS|
| | Declarative development paradigm | UI development: ArkTS
Service entries: files with fixed file names, which are **app.ets** (Page ability), **service.ts** (Service ability), and **data.ts** (Data ability)
Service logic: JS and TS|
| Service widget| Web-like development paradigm| UI development: HML, CSS, and JSON (action)
Service entry: **form.ts**
Service logic: JS and TS|
| | Declarative development paradigm | Not supported currently |
**Stage Model**
| Type | UI Development Paradigm | Description |
| ---- | -------- | ---------------------------------------- |
| Application | Web-like development paradigm| Not supported currently |
| | Declarative development paradigm | UI development: ArkTS
Service entries: derived from **ohos.application.Ability**/**ExtensionAbility**
Service logic: TS|
| Service widget| Web-like development paradigm| UI development: HML, CSS, and JSON (action)
Service entries: derived from **FormExtensionAbility**
Service logic: TS|
| | Declarative development paradigm | Not supported currently |