# Keyboard and Mouse Event
Keyboard and mouse events refer to the input events of external keyboards and mouse devices.
## Mouse Event
The supported mouse events include the events triggered by external mouse devices and touchpads.
Mouse events can trigger the following callbacks.
| Name | Description |
| ---------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------- |
| onHover(event: (isHover: boolean) => void) | Triggered when the mouse pointer enters or leaves the component.
**isHover**: whether the mouse pointer hovers over the component. The value **true** means that the mouse pointer enters the component, and the value **false** means that the mouse pointer leaves the component.|
| onMouse(event: (event?: MouseEvent) => void) | Triggered when the component is clicked by a mouse button or the mouse pointer moves over the component. The **event** parameter indicates the timestamp, mouse button, action, coordinates of the clicked point on the entire screen, and coordinates of the clicked point relative to the component when the event is triggered.|
When the component is bound to the **onHover** callback, you can use the [hoverEffect](../reference/apis-arkui/arkui-ts/ts-universal-attributes-hover-effect.md#hovereffect) attribute to set the hover effect of the component in hover state.
**Figure 1** Mouse event data flow

After a mouse event is passed to ArkUI, it is processed as follows:
- If the event is a left-click (pressing, releasing, or moving): The mouse event is first converted into a touch event in the same position. Then the touch event undergoes hit testing, gesture recognition, and callback responses. Finally the mouse event undergoes its own hit testing and callback responses.
- If the event is not a left-click: The event is only used for mouse-specific hit testing and callback responses.
>**NOTE**
>
>All single-finger touch events and gesture events may be triggered and responded to using the left-click. For example, to implement page redirection invoked by clicking a button with support for finger touches and left-clicks, you just need to bind an **onClick** event. If you want to implement different effects for the finger touch and the left-click, you can use the **source** parameter in the **onClick** callback to determine whether the current event is triggered by a finger or a mouse device.
### onHover
```ts
onHover(event: (isHover: boolean) => void)
```
Triggered when the mouse pointer enters or leaves the component. The **isHover** parameter indicates whether the mouse pointer hovers over the component. This event does not support custom bubbling settings. By default, event bubbling occurs between parent and child components.
If this API is bound to a component, it is triggered when the mouse pointer enters the component from outside and the value of **isHover** is **true**, or when the mouse pointer leaves the component and the value of **isHover** is **false**.
>**NOTE**
>
>Event bubbling is an event propagation in the document object model (DOM) when an event is first handled by an element and then passed to its parent element for further processing.
```ts
// xxx.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct MouseExample {
@State hoverText: string = 'Not Hover';
@State Color: Color = Color.Gray;
build() {
Column() {
Button(this.hoverText)
.width(200).height(100)
.backgroundColor(this.Color)
.onHover((isHover?: boolean) => { // Listen for whether the mouse cursor is hovered over the button.
if (isHover) {
this.hoverText = 'Hovered!';
this.Color = Color.Green;
}
else {
this.hoverText = 'Not Hover';
this.Color = Color.Gray;
}
})
}.width('100%').height('100%').justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
```
In this example, a **Button** component is created, with an initial gray background color and the content **Not Hover**. The component is bound to the **onHover** callback. In the callback, **this.isHovered** is set to the callback parameter **isHover**.
When the mouse pointer moves from outside the **Button** component to inside, the callback is invoked, setting the value of **isHover** to **true**. As a result, the background color of the component changes to **Color.Green**, and the content is updated to **Hovered!**.
When the mouse pointer moves from inside the **Button** component to outside, the callback is invoked again, setting the value of **isHover** to **false**. The component then reverts to its initial style.

### onMouse
```ts
onMouse(event: (event?: MouseEvent) => void)
```
Triggered when a mouse event occurs. It is triggered each time a mouse pointer action (**MouseAction**) is detected in the component. The parameter is a [MouseEvent](../reference/apis-arkui/arkui-ts/ts-universal-mouse-key.md#mouseevent) object, which indicates the mouse event that triggers the callback. This event supports custom bubbling settings. By default, event bubbling occurs between parent and child components. It is commonly used for custom mouse behavior logic.
You can use the **MouseEvent** object in the callback to obtain information about the triggered event, including the coordinates (**displayX**, **displayY**, **windowX**, **windowY**, **x**, and **y**), button ([MouseButton](../reference/apis-arkui/arkui-ts/ts-appendix-enums.md#mousebutton8)), action ([MouseAction](../reference/apis-arkui/arkui-ts/ts-appendix-enums.md#mouseaction8)), timestamp (**timestamp**), display area of the object that triggers the event ([EventTarget](../reference/apis-arkui/arkui-ts/ts-universal-events-click.md#eventtarget8)), and event source ([SourceType](../reference/apis-arkui/arkui-ts/ts-gesture-settings.md#sourcetype)). The **stopPropagation** callback of **MouseEvent** can be used to prevent the event from bubbling up.
>**NOTE**
>
>**MouseButton** indicates the physical mouse button being pressed or released that triggers the mouse event. The values are **Left**, **Right**, **Middle**, **Back**, **Forward**, and **None**. **None** indicates that no button is pressed or released, which means that the event is triggered by the mouse pointer moving on the component.
```ts
// xxx.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct MouseExample {
@State buttonText: string = '';
@State columnText: string = '';
@State hoverText: string = 'Not Hover';
@State Color: Color = Color.Gray;
build() {
Column() {
Button(this.hoverText)
.width(200)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(this.Color)
.onHover((isHover?: boolean) => {
if (isHover) {
this.hoverText = 'Hovered!';
this.Color = Color.Green;
}
else {
this.hoverText = 'Not Hover';
this.Color = Color.Gray;
}
})
.onMouse((event?: MouseEvent) => { // Set the onMouse callback for the button.
if (event) {
this.buttonText = 'Button onMouse:\n' + '' +
'button = ' + event.button + '\n' +
'action = ' + event.action + '\n' +
'x,y = (' + event.x + ',' + event.y + ')' + '\n' +
'windowXY=(' + event.windowX + ',' + event.windowY + ')';
}
})
Divider()
Text(this.buttonText).fontColor(Color.Green)
Divider()
Text(this.columnText).fontColor(Color.Red)
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.borderWidth(2)
.borderColor(Color.Red)
.onMouse((event?: MouseEvent) => { // Set the onMouse callback for the column.
if (event) {
this.columnText = 'Column onMouse:\n' + '' +
'button = ' + event.button + '\n' +
'action = ' + event.action + '\n' +
'x,y = (' + event.x + ',' + event.y + ')' + '\n' +
'windowXY=(' + event.windowX + ',' + event.windowY + ')';
}
})
}
}
```
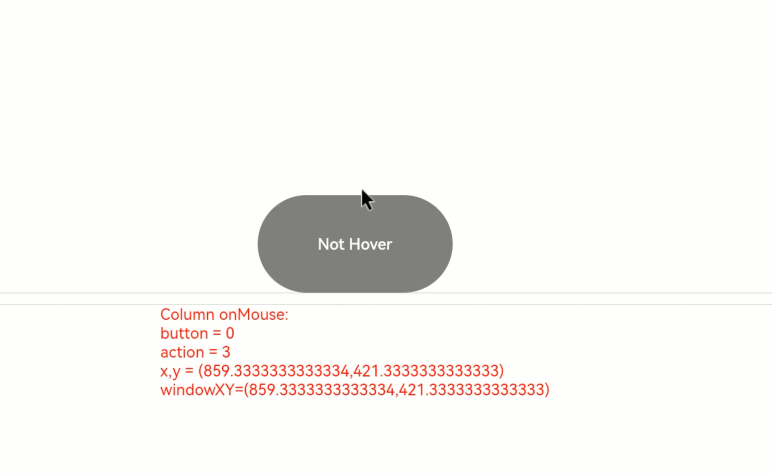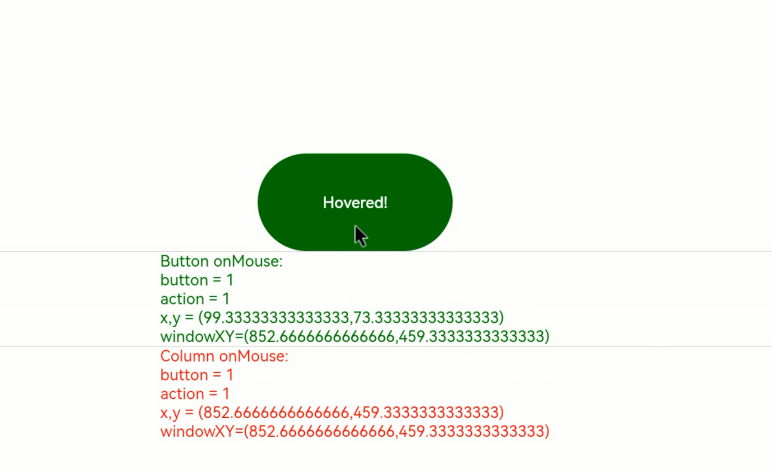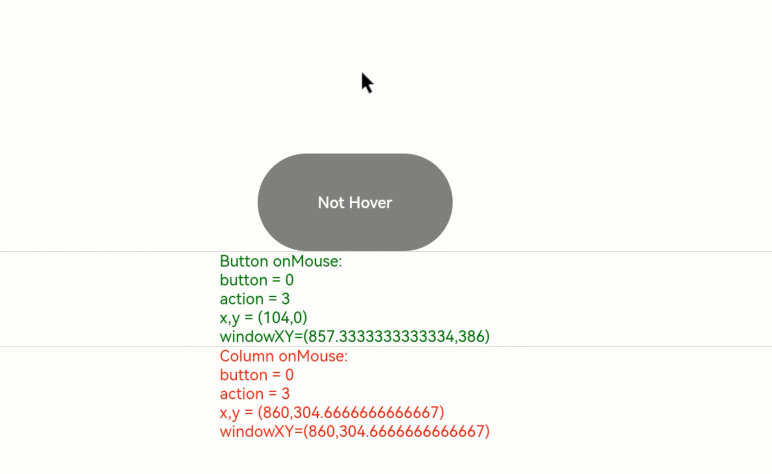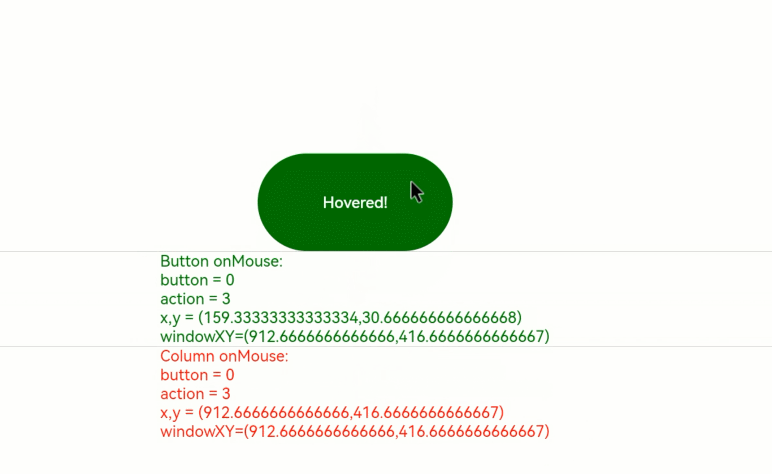
Bind the **onMouse** API to the **Button** component based on the **onHover** example, and display the values of the callback parameters, such as **button** and **action**. Apply the same settings to the outer **Column** container. The entire process can be divided into the following two actions:
1. Moving the mouse pointer: When the mouse pointer moves from outside the **Button** component to inside, only the **onMouse** callback of the **Column** component is triggered. When the mouse pointer enters the button, as the **onMouse** event bubbles up by default, both the **onMouse** callbacks of the **Column** and **Button** components are invoked. Because no mouse button is clicked during this process, the displayed information shows **button** as **0** (enumerated value of **MouseButton.None**) and **action** as **3** (enumerated value of **MouseAction.Move**).
2. Clicking the mouse button: After the mouse pointer enters the **Button** component, clicking the component twice (left-click and right-click) produces the following results:
Left-click: button = 1 (enumerated value of **MouseButton.Left**); action = 1 (enumerated value of **MouseAction.Press**); action = 2 (enumerated value of **MouseAction.Release**).
Right-click: button = 2 (enumerated value of **MouseButton.Right**); action = 1 (enumerated value of **MouseAction.Press**); action = 2 (enumerated value of **MouseAction.Release**)
To prevent the mouse event from bubbling, call the **stopPropagation()** API.
```ts
class ish{
isHovered:boolean = false
set(val:boolean){
this.isHovered = val;
}
}
class butf{
buttonText:string = ''
set(val:string){
this.buttonText = val
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct MouseExample {
@State isHovered:ish = new ish()
build(){
Column(){
Button(this.isHovered ? 'Hovered!' : 'Not Hover')
.width(200)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor(this.isHovered ? Color.Green : Color.Gray)
.onHover((isHover?: boolean) => {
if(isHover) {
let ishset = new ish()
ishset.set(isHover)
}
})
.onMouse((event?: MouseEvent) => {
if (event) {
if (event.stopPropagation) {
event.stopPropagation(); // Prevent the onMouse event from bubbling.
}
let butset = new butf()
butset.set('Button onMouse:\n' + '' +
'button = ' + event.button + '\n' +
'action = ' + event.action + '\n' +
'x,y = (' + event.x + ',' + event.y + ')' + '\n' +
'windowXY=(' + event.windowX + ',' + event.windowY + ')');
}
})
}
}
}
```
To prevent the mouse event of the child component (**Button**) from bubbling up to its parent component (**Column**), use the **event** parameter in the **onMouse** callback of **Button** to call the **stopPropagation** API.
```ts
event.stopPropagation()
```
With bubbling prevented, the mouse event on the **Button** component will trigger the **onMouse** callback of the **Button** component, but not the **onMouse** callback of the **Column** component.
### hoverEffect
```ts
hoverEffect(value: HoverEffect)
```
Sets the hover effect of the component in hover state. The parameter value type is **HoverEffect**. The **Auto**, **Scale**, and **Highlight** effects are preset and do not support customization.
**Table 1** HoverEffect
| Value| Description |
| -------------- | ---------------------------------------- |
| Auto | Default hover effect, which varies by component. |
| Scale | Scale effect. When the mouse pointer is placed over the component, the component is scaled up from 100% to 105%. When the mouse pointer is moved away, the component is scaled down from 105% to 100%.|
| Highlight | Background fade-in and fade-out effect. When the mouse pointer is placed over the component, a white layer with 5% opacity is applied to the background color of the component, resulting in a dimmed background. When the mouse pointer is moved away, the background color of the component is restored to the original style.|
| None | No effect. |
```ts
// xxx.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct HoverExample {
build() {
Column({ space: 10 }) {
Button('Auto')
.width(170).height(70)
Button('Scale')
.width(170).height(70)
.hoverEffect(HoverEffect.Scale)
Button('Highlight')
.width(170).height(70)
.hoverEffect(HoverEffect.Highlight)
Button('None')
.width(170).height(70)
.hoverEffect(HoverEffect.None)
}.width('100%').height('100%').justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
```

The default hover effect for the button is the **Highlight** effect. Therefore, the effects of **Auto** and **Highlight** are the same. The **Highlight** effect darkens the background color, **Scale** causes the component to scale, and **None** disables the hover effect.
## Key Event
### Key Event Data Flow

After being triggered by a device such as a peripheral keyboard, a key event has its data processed and converted by the driver and multimodal input modules, and then is sent to the currently focused window. The window dispatches the received event, following the sequence below. The dispatch stops once the event is consumed.
1. The window first dispatches the event to the ArkUI framework for invoking the **onKeyPreIme** callback bound to the component in focus as well as the page keyboard shortcuts.
2. If the ArkUI framework does not consume the event, the window dispatches the event to the input method for key input.
3. If the input method does not consume the event, the window dispatches the event to the ArkUI framework again for responding to the system default key event (for example, focus navigation) and for invoking the **onKeyEvent** callback bound to the component in focus.
When a text box has focus and the input method is enabled, most key events are consumed by the input method. For example, a letter key is used by the input method to enter a letter in the text box, and an arrow key is used by the input method to switch to the desired candidate word. Yet, if a keyboard shortcut is bound to the text box, the shortcut responds to the event first, and the event will not be consumed by the input method.
After the key event is sent to the ArkUI framework, it first identifies the complete focus chain, and then sends the key event from one node to the next, following the leaf-to-root path.
The key event process for the **Web** component differs from the aforementioned process. The **Web** component does not match keyboard shortcuts when **onKeyPreIme** returns **false**. The unconsumed key event will be re-dispatched back to ArkUI through **ReDispatch** during the third key press dispatch. It is within this **ReDispatch** that operations such as matching keyboard shortcuts are performed again.
### onKeyEvent & onKeyPreIme
```ts
onKeyEvent(event: (event: KeyEvent) => void): T
onKeyEvent(event: Callback): T
onKeyPreIme(event: Callback): T
onKeyEventDispatch(event: Callback): T
```
The difference between the preceding two methods lies only in the triggering time. For details, see [Key Event Data Flow](#key-event-data-flow). The return value of **onKeyPreIme** determines whether the key event will be dispatched for the page keyboard shortcut, input method, and **onKeyEvent**.
The methods are triggered when the bound component has focus and a key event occurs on the component. The callback parameter [KeyEvent](../reference/apis-arkui/arkui-ts/ts-universal-events-key.md#keyevent) can be used to obtain the information about the key event, including [KeyType](../reference/apis-arkui/arkui-ts/ts-appendix-enums.md#keytype), [keyCode](../reference/apis-input-kit/js-apis-keycode.md#keycode), **keyText**, [KeySource](../reference/apis-arkui/arkui-ts/ts-appendix-enums.md#keysource), **deviceId**, **metaKey**, **timestamp**, and **stopPropagation**.
```ts
// xxx.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct KeyEventExample {
@State buttonText: string = '';
@State buttonType: string = '';
@State columnText: string = '';
@State columnType: string = '';
build() {
Column() {
Button('onKeyEvent')
.defaultFocus(true)
.width(140).height(70)
.onKeyEvent((event?: KeyEvent) => { // Set the onKeyEvent event for the button.
if(event){
if (event.type === KeyType.Down) {
this.buttonType = 'Down';
}
if (event.type === KeyType.Up) {
this.buttonType = 'Up';
}
this.buttonText = 'Button: \n' +
'KeyType:' + this.buttonType + '\n' +
'KeyCode:' + event.keyCode + '\n' +
'KeyText:' + event.keyText;
}
})
Divider()
Text(this.buttonText).fontColor(Color.Green)
Divider()
Text(this.columnText).fontColor(Color.Red)
}.width('100%').height('100%').justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.onKeyEvent((event?: KeyEvent) => { // Set the onKeyEvent event for the parent container Column.
if(event){
if (event.type === KeyType.Down) {
this.columnType = 'Down';
}
if (event.type === KeyType.Up) {
this.columnType = 'Up';
}
this.columnText = 'Column: \n' +
'KeyType:' + this.buttonType + '\n' +
'KeyCode:' + event.keyCode + '\n' +
'KeyText:' + event.keyText;
}
})
}
}
```
In the preceding example, **onKeyEvent** is bound to the **Button** component and its parent container **Column**. After the application opens and loads a page, the first focusable non-container component in the component tree automatically obtains focus. Set the **Button** component as the default focus of the current page. Because the **Button** component is a child node of the **Column** component, the **Column** component also obtains focus. For details about the focus obtaining mechanism, see [Focus Event](arkts-common-events-focus-event.md).

After the application is opened, press the following keys in sequence: Space, Enter, Left Ctrl, Left Shift, Letter A, and Letter Z.
1. Because the **onKeyEvent** event bubbles by default, the **onKeyEvent** callbacks of both **Button** and **Column** are invoked.
2. Each key has two callbacks, which correspond to **KeyType.Down** and **KeyType.Up** respectively, indicating that the key is pressed and then lifted.
To prevent the key event of the **Button** component from bubbling up to its parent container **Column**, add the **event.stopPropagation()** API to the **onKeyEvent** callback of **Button**.
```ts
@Entry
@Component
struct KeyEventExample {
@State buttonText: string = '';
@State buttonType: string = '';
@State columnText: string = '';
@State columnType: string = '';
build() {
Column() {
Button('onKeyEvent')
.defaultFocus(true)
.width(140).height(70)
.onKeyEvent((event?: KeyEvent) => {
// Use stopPropagation to prevent the key event from bubbling up.
if(event){
if(event.stopPropagation){
event.stopPropagation();
}
if (event.type === KeyType.Down) {
this.buttonType = 'Down';
}
if (event.type === KeyType.Up) {
this.buttonType = 'Up';
}
this.buttonText = 'Button: \n' +
'KeyType:' + this.buttonType + '\n' +
'KeyCode:' + event.keyCode + '\n' +
'KeyText:' + event.keyText;
}
})
Divider()
Text(this.buttonText).fontColor(Color.Green)
Divider()
Text(this.columnText).fontColor(Color.Red)
}.width('100%').height('100%').justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.onKeyEvent((event?: KeyEvent) => { // Set the onKeyEvent event for the parent container Column.
if(event){
if (event.type === KeyType.Down) {
this.columnType = 'Down';
}
if (event.type === KeyType.Up) {
this.columnType = 'Up';
}
this.columnText = 'Column: \n' +
'KeyType:' + this.buttonType + '\n' +
'KeyCode:' + event.keyCode + '\n' +
'KeyText:' + event.keyText;
}
})
}
}
```

This example shows how to use **OnKeyPreIme** to block the left arrow key input in the text box.
```ts
import { KeyCode } from '@kit.InputKit';
@Entry
@Component
struct PreImeEventExample {
@State buttonText: string = '';
@State buttonType: string = '';
@State columnText: string = '';
@State columnType: string = '';
build() {
Column() {
Search({
placeholder: "Search..."
})
.width("80%")
.height("40vp")
.border({ radius:"20vp" })
.onKeyPreIme((event:KeyEvent) => {
if (event.keyCode == KeyCode.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT) {
return true;
}
return false;
})
}
}
}
```
This example demonstrates how to use **onKeyEventDispatch** to distribute key events to child components, which handle the events using **onKeyEvent**.
```ts
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
Row() {
Button('button1').id('button1').onKeyEvent((event) => {
console.log("button1");
return true
})
Button('button1').id('button2').onKeyEvent((event) => {
console.log("button2");
return true
})
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.id('Row1')
.onKeyEventDispatch((event) => {
let context = this.getUIContext();
context.getFocusController().requestFocus('button1');
return context.dispatchKeyEvent('button1', event);
})
}
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
.onKeyEventDispatch((event) => {
if (event.type == KeyType.Down) {
let context = this.getUIContext();
context.getFocusController().requestFocus('Row1');
return context.dispatchKeyEvent('Row1', event);
}
return true;
})
}
}
```