```
- Use the actual height style for the parent element.
```
```
## Handling the Compatibility of HTML5 Code
To avoid white screen issues, you can handle the compatibility issue as follows:
* Intercept special protocols.
* If a white screen is displayed due to the **tel:** or **mailto:** protocol invoked by the HTML5 page, intercept the protocol and invoke the system dialing capability through **onInterceptRequest**.
```c
.onInterceptRequest((event) => {
if (event.request.url.startWith('tel:')) {
// Invoke the system dialing capability.
call.makeCall({ phoneNumber: '123456' });
return { responseCode: 404 }; // Prevent the default behavior.
}
return null;
})
```
## Monitoring Memory and Lifecycle
If the memory usage reaches the threshold, the rendering process will be terminated, causing a white screen. Similarly, a white screen will occur if the rendering process fails to start or is abnormally terminated. You can check the cause in logs. For example, check whether the **Web** component is correctly bound to the **WebController** or whether the white screen occurs because the **Web** component is released too early. Check the information related to the render process in the log, for example, whether a memory leak causes insufficient rendering memory. The keyword **MEMORY_PRESSURE_LEVEL_CRITICAL** indicates that the memory usage has reached the threshold. In this case, the web page may encounter exceptions such as black screen, artifacts, or flicker. You need to check whether a memory leak occurs and whether the render process is successfully started or exits abnormally.
The following table lists log keywords and the corresponding descriptions.
| Keyword | Description |
| ---- | -------------------------------- |
| StartRenderProcess failed | The rendering process fails to be started.|
| MEMORY_PRESSURE_LEVEL_CRITICAL | The device memory pressure reaches the threshold. If the device continues to be used, a black screen, screen flickering, or white screen may occur.|
| crashpad SandboxedHandler::HandlerCrash, received signo = xxx | The render process crashes, causing problems such as white screen and **Web** component suspension.|
| SharedContextState context lost via Skia OOM | The shared memory is insufficient, which may cause the application to crash, produce artifacts, or become suspended.
| CreateNativeViewGLSurfaceEGLOhos::normal surface | The EGL surface is successfully created. If this log is not displayed, a white screen occurs.|
| INFO: request had no response within 5 seconds | Network timeout.|
| final url: ***, error_code xxx(net::ERR_XXX) | An error is reported during the main resource loading.|
The following figure shows the key points contained during the **Web** component loading process. The following table lists the log keywords during the **Web** component loading process.
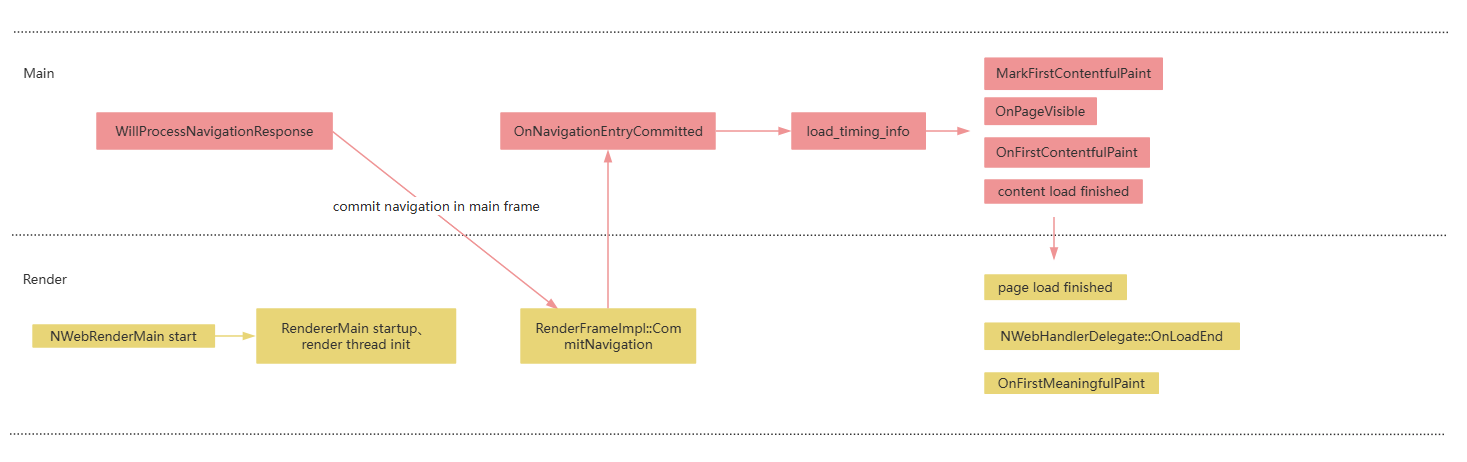
| Keyword | Description |
| ---- | -------------------------------- |
| NWebRenderMain start | The child process starts.|
| RendererMain startup,
render thread init | The child process initialization starts.|
| event_message: WillProcessNavigationResponse source_id xxx navigation_handle id: xxx| The response of the main resource is received.|
| event_message: commit navigation in main frame, routing_id: 4, url: *** | The navigation is committed to the child process.
| RenderFrameImpl::CommitNavigation,
event_message: page load start | The child process receives the commit message.|
| NWebHandlerDelegate::OnNavigationEntryCommitted,
event_message: Commit source_id xxx | The main process receives **DidCommitNavigation**.|
| event_message: load_timing_info errpr_code:0,...| The main resource loading is complete, and the time required for each phase is displayed.|
| event_message: MarkFirstContentfulPaint| The tag identifies an element with displayable content.|
| NWebHandlerDelegate::OnPageVisible| The first frame is displayed.|
| NWebHandlerDelegate::OnFirstContentfulPaint| The first frame content is displayed.|
| event_message: content load finished | The page content parsing is complete.|
| event_message: page load finished,
NWebHandlerDelegate::OnLoadEnd,
NWebHandlerDelegate::MainFrame OnLoadEnd,
NWebHandlerDelegate::OnFirstMeaningfulPaint | The page and sub-resources are loaded.|