README.md
1
2xxHash - Extremely fast hash algorithm
3======================================
4
5xxHash is an Extremely fast Hash algorithm, running at RAM speed limits.
6It successfully completes the [SMHasher](https://code.google.com/p/smhasher/wiki/SMHasher) test suite
7which evaluates collision, dispersion and randomness qualities of hash functions.
8Code is highly portable, and hashes are identical across all platforms (little / big endian).
9
10|Branch |Status |
11|------------|---------|
12|dev | [](https://travis-ci.org/Cyan4973/xxHash?branch=dev) |
13
14
15Benchmarks
16-------------------------
17
18The reference system uses an Intel i7-9700K cpu, and runs Ubuntu x64 20.04.
19The [open source benchmark program] is compiled with `clang` v10.0 using `-O3` flag.
20
21| Hash Name | Width | Bandwidth (GB/s) | Small Data Velocity | Quality | Comment |
22| --------- | ----- | ---------------- | ----- | --- | --- |
23| __XXH3__ (SSE2) | 64 | 31.5 GB/s | 133.1 | 10
24| __XXH128__ (SSE2) | 128 | 29.6 GB/s | 118.1 | 10
25| _RAM sequential read_ | N/A | 28.0 GB/s | N/A | N/A | _for reference_
26| City64 | 64 | 22.0 GB/s | 76.6 | 10
27| T1ha2 | 64 | 22.0 GB/s | 99.0 | 9 | Slightly worse [collisions]
28| City128 | 128 | 21.7 GB/s | 57.7 | 10
29| __XXH64__ | 64 | 19.4 GB/s | 71.0 | 10
30| SpookyHash | 64 | 19.3 GB/s | 53.2 | 10
31| Mum | 64 | 18.0 GB/s | 67.0 | 9 | Slightly worse [collisions]
32| __XXH32__ | 32 | 9.7 GB/s | 71.9 | 10
33| City32 | 32 | 9.1 GB/s | 66.0 | 10
34| Murmur3 | 32 | 3.9 GB/s | 56.1 | 10
35| SipHash | 64 | 3.0 GB/s | 43.2 | 10
36| FNV64 | 64 | 1.2 GB/s | 62.7 | 5 | Poor avalanche properties
37| Blake2 | 256 | 1.1 GB/s | 5.1 | 10 | Cryptographic
38| SHA1 | 160 | 0.8 GB/s | 5.6 | 10 | Cryptographic but broken
39| MD5 | 128 | 0.6 GB/s | 7.8 | 10 | Cryptographic but broken
40
41[open source benchmark program]: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/tree/release/tests/bench
42[collisions]: https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/wiki/Collision-ratio-comparison#collision-study
43
44note 1: Small data velocity is a _rough_ evaluation of algorithm's efficiency on small data. For more detailed analysis, please refer to next paragraph.
45
46note 2: some algorithms feature _faster than RAM_ speed. In which case, they can only reach their full speed when input data is already in CPU cache (L3 or better). Otherwise, they max out on RAM speed limit.
47
48### Small data
49
50Performance on large data is only one part of the picture.
51Hashing is also very useful in constructions like hash tables and bloom filters.
52In these use cases, it's frequent to hash a lot of small data (starting at a few bytes).
53Algorithm's performance can be very different for such scenarios, since parts of the algorithm,
54such as initialization or finalization, become fixed cost.
55The impact of branch mis-prediction also becomes much more present.
56
57XXH3 has been designed for excellent performance on both long and small inputs,
58which can be observed in the following graph:
59
60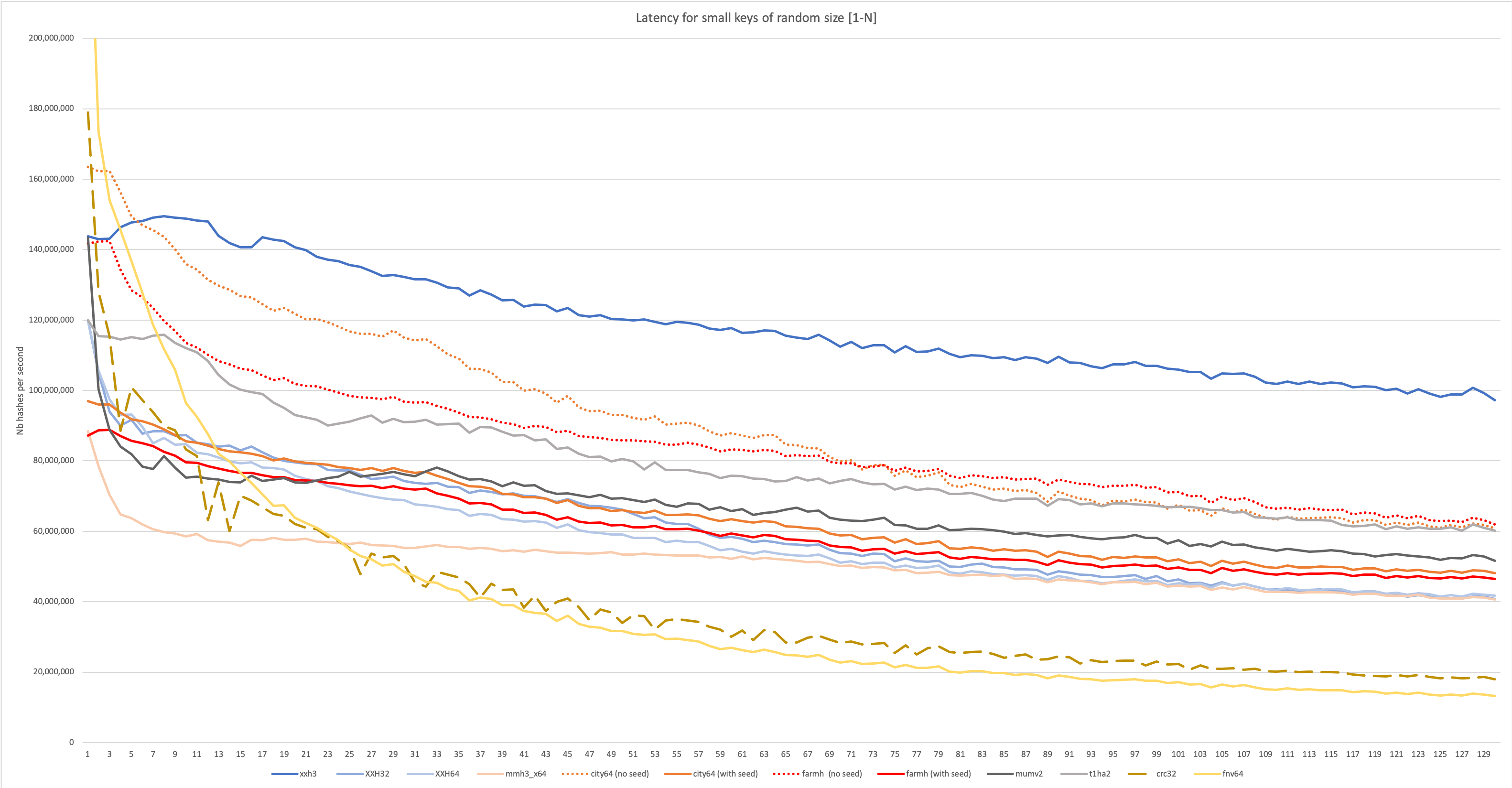
61
62For a more detailed analysis, visit the wiki :
63https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/wiki/Performance-comparison#benchmarks-concentrating-on-small-data-
64
65Quality
66-------------------------
67
68Speed is not the only property that matters.
69Produced hash values must respect excellent dispersion and randomness properties,
70so that any sub-section of it can be used to maximally spread out a table or index,
71as well as reduce the amount of collisions to the minimal theoretical level, following the [birthday paradox].
72
73`xxHash` has been tested with Austin Appleby's excellent SMHasher test suite,
74and passes all tests, ensuring reasonable quality levels.
75It also passes extended tests from [newer forks of SMHasher], featuring additional scenarios and conditions.
76
77Finally, xxHash provides its own [massive collision tester](https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/tree/dev/tests/collisions),
78able to generate and compare billions of hash to test the limits of 64-bit hash algorithms.
79On this front too, xxHash features good results, in line with the [birthday paradox].
80A more detailed analysis is documented [in the wiki](https://github.com/Cyan4973/xxHash/wiki/Collision-ratio-comparison).
81
82[birthday paradox]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Birthday_problem
83[newer forks of SMHasher]: https://github.com/rurban/smhasher
84
85
86### Build modifiers
87
88The following macros can be set at compilation time to modify libxxhash's behavior. They are generally disabled by default.
89
90- `XXH_INLINE_ALL`: Make all functions `inline`, with implementations being directly included within `xxhash.h`.
91 Inlining functions is beneficial for speed on small keys.
92 It's _extremely effective_ when key length is expressed as _a compile time constant_,
93 with performance improvements observed in the +200% range .
94 See [this article](https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2018/03/xxhash-for-small-keys-impressive-power.html) for details.
95- `XXH_PRIVATE_API`: same outcome as `XXH_INLINE_ALL`. Still available for legacy support.
96 The name underlines that `XXH_*` symbols will not be exported.
97- `XXH_NAMESPACE`: Prefixes all symbols with the value of `XXH_NAMESPACE`.
98 This macro can only use compilable character set.
99 Useful to evade symbol naming collisions,
100 in case of multiple inclusions of xxHash's source code.
101 Client applications still use the regular function names,
102 as symbols are automatically translated through `xxhash.h`.
103- `XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS`: The default method `0` uses a portable `memcpy()` notation.
104 Method `1` uses a gcc-specific `packed` attribute, which can provide better performance for some targets.
105 Method `2` forces unaligned reads, which is not standards compliant, but might sometimes be the only way to extract better read performance.
106 Method `3` uses a byteshift operation, which is best for old compilers which don't inline `memcpy()` or big-endian systems without a byteswap instruction
107- `XXH_FORCE_ALIGN_CHECK`: Use a faster direct read path when input is aligned.
108 This option can result in dramatic performance improvement when input to hash is aligned on 32 or 64-bit boundaries,
109 when running on architectures unable to load memory from unaligned addresses, or suffering a performance penalty from it.
110 It is (slightly) detrimental on platform with good unaligned memory access performance (same instruction for both aligned and unaligned accesses).
111 This option is automatically disabled on `x86`, `x64` and `aarch64`, and enabled on all other platforms.
112- `XXH_VECTOR` : manually select a vector instruction set (default: auto-selected at compilation time). Available instruction sets are `XXH_SCALAR`, `XXH_SSE2`, `XXH_AVX2`, `XXH_AVX512`, `XXH_NEON` and `XXH_VSX`. Compiler may require additional flags to ensure proper support (for example, `gcc` on linux will require `-mavx2` for AVX2, and `-mavx512f` for AVX512).
113- `XXH_NO_PREFETCH` : disable prefetching. XXH3 only.
114- `XXH_PREFETCH_DIST` : select prefecting distance. XXH3 only.
115- `XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS`: By default, xxHash uses `__attribute__((always_inline))` and `__forceinline` to improve performance at the cost of code size.
116 Defining this macro to 1 will mark all internal functions as `static`, allowing the compiler to decide whether to inline a function or not.
117 This is very useful when optimizing for smallest binary size,
118 and is automatically defined when compiling with `-O0`, `-Os`, `-Oz`, or `-fno-inline` on GCC and Clang.
119 This may also increase performance depending on compiler and architecture.
120- `XXH_REROLL`: Reduces the size of the generated code by not unrolling some loops.
121 Impact on performance may vary, depending on platform and algorithm.
122- `XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER`: if set to `1`, when input is a `NULL` pointer,
123 xxHash'd result is the same as a zero-length input
124 (instead of a dereference segfault).
125 Adds one branch at the beginning of each hash.
126- `XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY`: gives access to the state declaration for static allocation.
127 Incompatible with dynamic linking, due to risks of ABI changes.
128- `XXH_NO_LONG_LONG`: removes compilation of algorithms relying on 64-bit types (XXH3 and XXH64). Only XXH32 will be compiled.
129 Useful for targets (architectures and compilers) without 64-bit support.
130- `XXH_IMPORT`: MSVC specific: should only be defined for dynamic linking, as it prevents linkage errors.
131- `XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN`: By default, endianess is determined by a runtime test resolved at compile time.
132 If, for some reason, the compiler cannot simplify the runtime test, it can cost performance.
133 It's possible to skip auto-detection and simply state that the architecture is little-endian by setting this macro to 1.
134 Setting it to 0 states big-endian.
135
136For the Command Line Interface `xxhsum`, the following environment variables can also be set :
137- `DISPATCH=1` : use `xxh_x86dispatch.c`, to automatically select between `scalar`, `sse2`, `avx2` or `avx512` instruction set at runtime, depending on local host. This option is only valid for `x86`/`x64` systems.
138
139
140### Building xxHash - Using vcpkg
141
142You can download and install xxHash using the [vcpkg](https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg) dependency manager:
143
144 git clone https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg.git
145 cd vcpkg
146 ./bootstrap-vcpkg.sh
147 ./vcpkg integrate install
148 ./vcpkg install xxhash
149
150The xxHash port in vcpkg is kept up to date by Microsoft team members and community contributors. If the version is out of date, please [create an issue or pull request](https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg) on the vcpkg repository.
151
152
153### Example
154
155The simplest example calls xxhash 64-bit variant as a one-shot function
156generating a hash value from a single buffer, and invoked from a C/C++ program:
157
158```C
159#include "xxhash.h"
160
161 (...)
162 XXH64_hash_t hash = XXH64(buffer, size, seed);
163}
164```
165
166Streaming variant is more involved, but makes it possible to provide data incrementally:
167
168```C
169#include "stdlib.h" /* abort() */
170#include "xxhash.h"
171
172
173XXH64_hash_t calcul_hash_streaming(FileHandler fh)
174{
175 /* create a hash state */
176 XXH64_state_t* const state = XXH64_createState();
177 if (state==NULL) abort();
178
179 size_t const bufferSize = SOME_SIZE;
180 void* const buffer = malloc(bufferSize);
181 if (buffer==NULL) abort();
182
183 /* Initialize state with selected seed */
184 XXH64_hash_t const seed = 0; /* or any other value */
185 if (XXH64_reset(state, seed) == XXH_ERROR) abort();
186
187 /* Feed the state with input data, any size, any number of times */
188 (...)
189 while ( /* some data left */ ) {
190 size_t const length = get_more_data(buffer, bufferSize, fh);
191 if (XXH64_update(state, buffer, length) == XXH_ERROR) abort();
192 (...)
193 }
194 (...)
195
196 /* Produce the final hash value */
197 XXH64_hash_t const hash = XXH64_digest(state);
198
199 /* State could be re-used; but in this example, it is simply freed */
200 free(buffer);
201 XXH64_freeState(state);
202
203 return hash;
204}
205```
206
207
208### License
209
210The library files `xxhash.c` and `xxhash.h` are BSD licensed.
211The utility `xxhsum` is GPL licensed.
212
213
214### Other programming languages
215
216Beyond the C reference version,
217xxHash is also available from many different programming languages,
218thanks to great contributors.
219They are [listed here](http://www.xxhash.com/#other-languages).
220
221
222### Packaging status
223
224Many distributions bundle a package manager
225which allows easy xxhash installation as both a `libxxhash` library
226and `xxhsum` command line interface.
227
228[](https://repology.org/project/xxhash/versions)
229
230
231### Special Thanks
232
233- Takayuki Matsuoka, aka @t-mat, for creating `xxhsum -c` and great support during early xxh releases
234- Mathias Westerdahl, aka @JCash, for introducing the first version of `XXH64`
235- Devin Hussey, aka @easyaspi314, for incredible low-level optimizations on `XXH3` and `XXH128`
236